The utility industry is embracing robotics, and robot usage across the industry is steadily rising each year. The utility industry includes electrical, water, & gas utility companies and renewable energy sources like hydroelectric facilities, solar farms, wind farms, and nuclear energy facilities.
What Can Robots Do for Utilities?
Robots are best used for dangerous, dirty, or dull tasks across all industries and the utility industry certainly has many of these types of tasks. Utilities (and companies across other industries) are not replacing workers with robots, they are augmenting workers to make their environments safer or their work more efficient.
Uses for Robots in Utility Companies
-
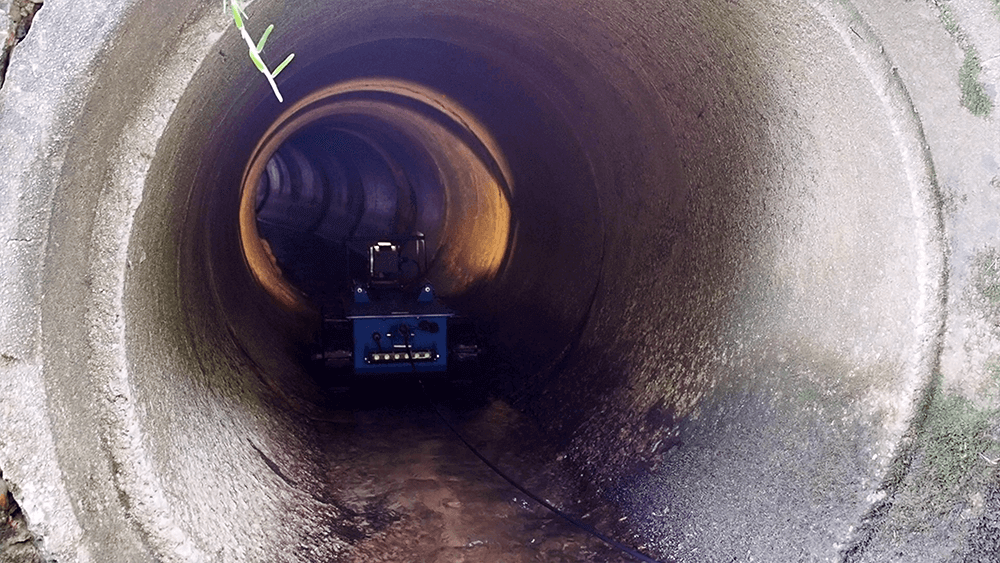
- Culvert & Pipe Inspection – Culverts and pipes are typically narrow and long, stretching underground or throughout a building. Sending a worker inside them to inspect the full length is impossible, risky, or inefficient. But, by using a tethered robot, workers can get a clear view of these tight spaces while staying on the outside.

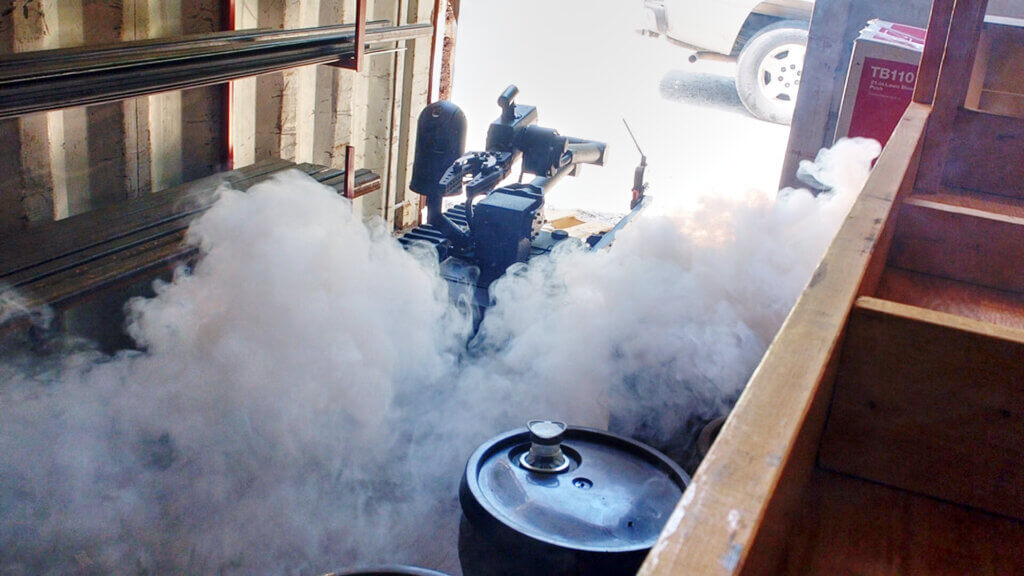
- Hazardous Material, Thermal, & Corona Inspections – Utility companies can use robots equipped with specialized sensors to inspect hazardous or inaccessible environments without risking humans to harmful exposure.

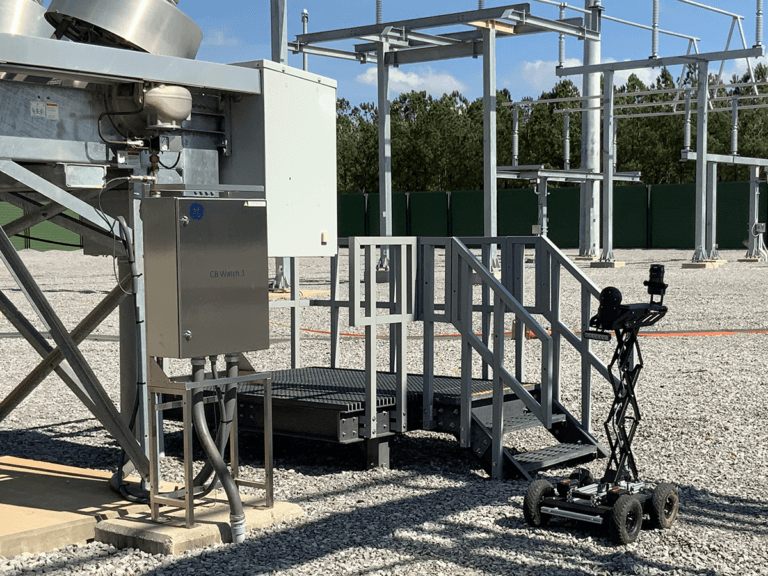
- SF6 Gas Monitoring at Different Heights – Many gas and electrical utilities use MultiRAE gas sensors to identify SF6 gas levels. By attaching these sensors to robots that can raise and lower to specific heights, workers can locate gas leaks and their severity.
- Under Vehicle & Heavy Machinery Inspections – Inspecting the underside of vehicles or heavy machinery can be difficult and risky. A person has to crawl under, sometimes in a tight space without room to move. That risk grows exponentially if the machinery or vehicle has to be lifted to allow access. With a compact inspection robot, workers can perform periodic maintenance checks quickly and safely.
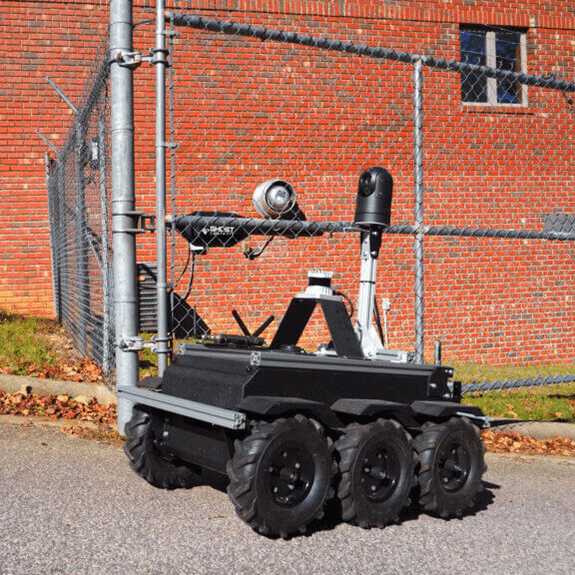
- Security Patrols – Patrol high-risk areas and secure facilities via autonomous or remotely controlled robots. These mobile security platforms give you “eyes and ears” from a safe distance. Some systems can even allow you to monitor situations from another state.
- Monitor Confined Spaces – Robots can also perform unmanned inspections of remote facilities, such as underground substations or solar farms.


Taking the Next Step
All of the use cases above are actual ways our utility clients are using robots. Here are some potential use cases that we’ve discussed with utilities, but have not built robots for just yet:
Autonomous Reality Capture & Facility Asset Management – Many facility managers are using reality capture software to create 360° walkthrough tours of their facilities, but capturing that data is tedious, so it’s not done often. Using autonomous robots, facility managers can capture their facility weekly or monthly and create a timeline of changes paired with asset management capabilities.
- “Follow Me” Robot for Heavy Loads / Toolbox – whether carrying a toolbox across the facility or hauling materials for miles along a pipeline, robots can carry heavy loads where utility trucks can’t fit or access.
- Handling Heavy Materials Outdoors – autonomously carry heavy solar panels across a solar farm to aid with installation and repairs, allowing panels to be spaced closer together since they do not need to be accessible by a vehicle.
- Clean Solar Panels – autonomously clean solar panels to improve the panels’ efficiency.
As you can see, utility companies have many ways to use robots. Once a company has a robot, they can find other dangerous, dirty, or dull tasks to use it for. That protects their workers from increased risk, improves employee retention and helps lower the utility’s workers’ compensation insurance cost.

 Autonomous Reality Capture & Facility Asset Management – Many facility managers are using reality capture software to create 360° walkthrough tours of their facilities, but capturing that data is tedious, so it’s not done often. Using autonomous robots, facility managers can capture their facility weekly or monthly and create a timeline of changes paired with asset management capabilities.
Autonomous Reality Capture & Facility Asset Management – Many facility managers are using reality capture software to create 360° walkthrough tours of their facilities, but capturing that data is tedious, so it’s not done often. Using autonomous robots, facility managers can capture their facility weekly or monthly and create a timeline of changes paired with asset management capabilities.