Pololu 5V, 600mA Step-Down Voltage Regulator D24V6F5 - DISCONTINUED
Features and Specifications
- Fixed 5 V with 4% accuracy
- Maximum output current: 600 mA
- 2 mA typical no-load quiescent current
- 550 kHz switching frequency
- 2 mA typical no-load quiescent current (20 µA typical quiescent current with SHDN = LOW)
- Integrated over-temperature and over-current shutoff
- Small size: 0.5" x 0.4" x 0.1" (13 mm x 10 mm x 3 mm)
- Size: 0.4" x 0.5" x 0.1"
- Weight: 0.5g
- Minimum operating voltage: 6.0 V
- Maximum operating voltage: 42 V
- Maximum output current: 600 mA
- Output voltage: 5 V
- Reverse voltage protection: N
- Maximum quiescent current: 2 mA
Using the Regulator Connections
The buck regulator has four connections: shutdown (SHDN), input voltage (VIN), ground (GND), and output voltage (VOUT).
The SHDN pin can be driven low (under 0.3 V) to turn off the output and put the board into a low-power state that typically draws 20 µA. The SHDN pin can be driven high (above 2.3 V) to enable the board, or it can be connected to VIN or left disconnected if you want to leave the board permanently enabled.
The input voltage, VIN, should exceed VOUT by at least the regulator's dropout voltage, and you must ensure that noise on your input does not exceed the 42 V maximum. Additionally, please be wary of destructive LC spikes.
The output voltage, VOUT, is fixed and depends on the regulator version: the D24VxF5 version outputs 5 V.
The four connections are labeled on the back side of the PCB, and they are arranged with a 0.1" spacing along the edge of the board for compatibility with solderless breadboards, connectors, and other prototyping arrangements that use a 0.1" grid. You can solder wires directly to the board or solder in either the 4x1 straight male header strip or the 4x1 right-angle male header strip that is included.
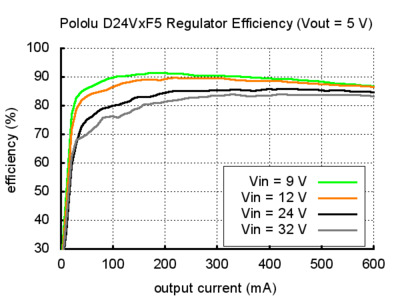
Typical Efficiency and Output Current
Typical Dropout Voltage
The dropout voltage of a step-down regulator is the minimum amount by which the input voltage must exceed the regulator's target output voltage in order to ensure the target output can be achieved. For example, if a 5 V regulator has a 1 V dropout voltage, the input must be at least 6 V to ensure the output is the full 5 V. The following graphs show the dropout voltages for the eight D24VxFx regulators as a function of the output current:
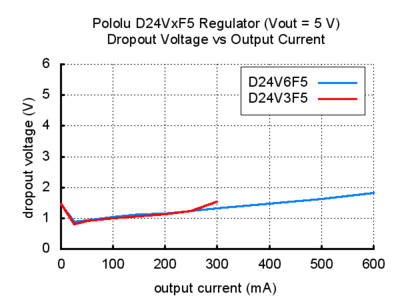
As you can see from the last two graphs, the dropout voltage of the low-current 9 V and 12 V versions (D24V3F9 and D24V3F12) spikes as the output current nears the 300 mA limit.
LC Voltage Spikes
When connecting voltage to electronic circuits, the initial rush of current can cause voltage spikes that are much higher than the input voltage. If these spikes exceed the regulator's maximum voltage (42 V), the regulator can be destroyed. In our tests with typical power leads (~30? Test clips), input voltages above 20 V caused spikes over 42 V. If you are connecting more than 20 V or your power leads or supply has high inductance, we recommend soldering a 33µF or larger electrolytic capacitor close to the regulator between VIN and GND. The capacitor should be rated for at least 50 V.
This item is no longer available. It has been replaced by Pololu 5V, 500mA Step-Down Voltage Regulator D24V5F5
These buck (step-down) voltage regulators generate lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 42 V. They are switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) and have a typical efficiency between 80% to 90%, which is much more efficient than linear voltage regulators, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large.
Pololu 5V, 600mA Step-Down Voltage Regulator D24V6F5 - DISCONTINUED
- Product Code: TE-176-005
- Brand: Pololu
- MPN: 2107
- Availability: Discontinued

